Step 6: Complete Pipeline Testing & Best Practices (10 minutes)
Code Location: code/v0.7.0/ (current)
Time: 70:00-80:00
Goal: Test the complete system and learn production best practices
Overview
In this final step, you’ll:
- Test the complete pipeline end-to-end
- Learn debugging techniques
- Understand performance optimization
- Explore production deployment considerations
- Review best practices
Architecture Review
Here’s what you’ve built:
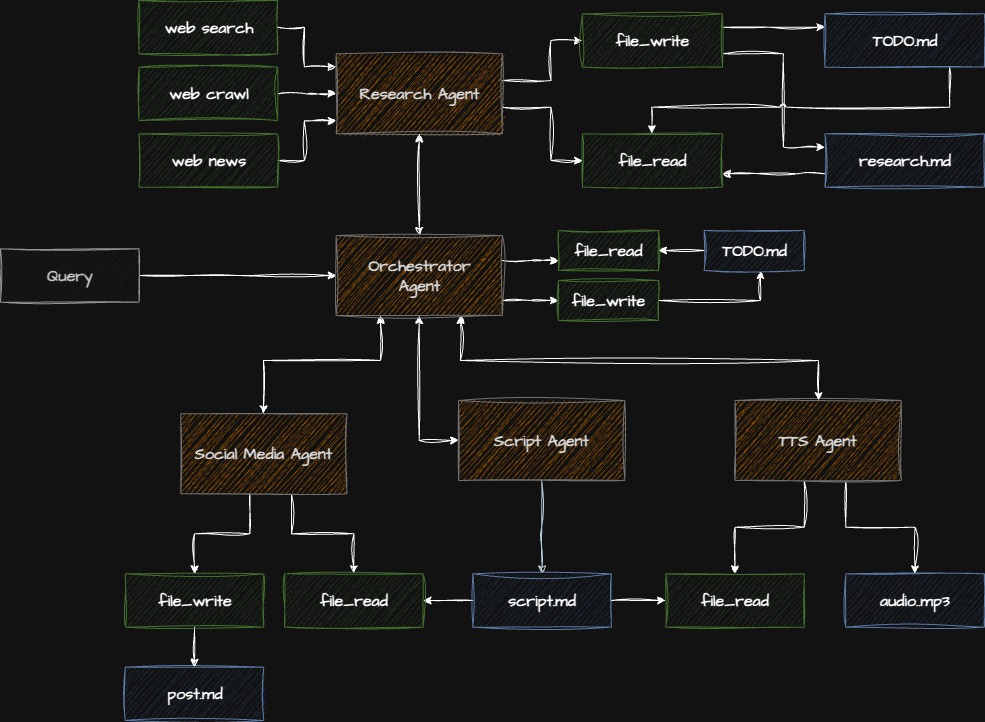
Step 6.1: Comprehensive Testing
Test Script 1: Minimal Pipeline
Test with bare minimum to verify each component:
File: tests/test_minimal.py
"""Minimal integration test."""
import logging
from app.script_agent.agent import create_script_agent
from app.social_agent.agent import create_social_agent
from app.tts_agent.agent import create_tts_agent
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def test_script_agent():
"""Test script generation."""
logger.info("Testing script agent...")
agent = create_script_agent()
result = agent.execute("Testing: Quick podcast about Python")
assert result.output
assert len(result.output) > 100
logger.info(f"✅ Script: {len(result.output)} chars")
def test_social_agent():
"""Test social media generation."""
logger.info("Testing social agent...")
agent = create_social_agent()
result = agent.execute("Create a test LinkedIn post about AI")
assert result.output
assert len(result.output) > 50
logger.info(f"✅ Social: {len(result.output)} chars")
def test_tts_agent():
"""Test audio generation."""
logger.info("Testing TTS agent...")
agent = create_tts_agent()
result = agent.execute(
"Convert this to audio: Hello, this is a test. Save to test_output.mp3"
)
assert "Success" in result.output
logger.info(f"✅ Audio: {result.output}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_script_agent()
test_social_agent()
test_tts_agent()
print("\n✅ All minimal tests passed!")Run:
python tests/test_minimal.pyTest Script 2: Full Pipeline
Test the complete orchestrated workflow:
File: tests/test_full_pipeline.py
"""Full pipeline integration test."""
import logging
import time
from app.model.agent_input import PipelineInput
from app.orchestrator_agent.agent import create_orchestrator
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def test_full_pipeline():
"""Test complete orchestrated pipeline."""
# Create test input
pipeline_input = PipelineInput(
topic="Introduction to Python Async Programming",
priority="both",
research_depth="quick", # Quick for testing
output_path="test_full_output.mp3"
)
# Execute
start = time.time()
orchestrator = create_orchestrator()
result = orchestrator.execute(pipeline_input)
duration = time.time() - start
# Verify results
assert result.success, f"Pipeline failed: {result.errors}"
assert result.script_length > 0, "No script generated"
assert result.social_post, "No social post generated"
assert result.audio_file, "No audio file generated"
print(f"\n✅ Full pipeline test passed!")
print(f"⏱️ Duration: {duration:.1f}s")
print(f"📊 Script: {result.script_length} chars")
print(f"📱 Social: {len(result.social_post)} chars")
print(f"🎵 Audio: {result.audio_file}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_full_pipeline()Run:
python tests/test_full_pipeline.pyTest Script 3: Error Handling
Test how the system handles failures:
File: tests/test_error_handling.py
"""Error handling test."""
import logging
from app.model.agent_input import PipelineInput
from app.orchestrator_agent.agent import create_orchestrator
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def test_invalid_topic():
"""Test with empty/invalid topic."""
pipeline_input = PipelineInput(
topic="", # Invalid
priority="both",
)
try:
orchestrator = create_orchestrator()
result = orchestrator.execute(pipeline_input)
assert not result.success or len(result.errors) > 0
print("✅ Handled empty topic correctly")
except Exception as e:
print(f"✅ Caught expected error: {e}")
def test_partial_failure():
"""Test pipeline continues on optional failures."""
# This would require mocking failures
# For workshop, we'll just document the pattern
print("✅ Partial failure handling implemented in orchestrator")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_invalid_topic()
test_partial_failure()
print("\n✅ Error handling tests passed!")Step 6.2: Debugging Techniques
Enable Detailed Logging
import logging
# Configure detailed logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG, # Show all logs
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[
logging.StreamHandler(), # Console
logging.FileHandler('pipeline.log') # File
]
)Add Debug Checkpoints
def execute_with_checkpoints(pipeline_input: PipelineInput):
"""Execute pipeline with debugging checkpoints."""
logger.debug(f"Input: {pipeline_input.model_dump_json(indent=2)}")
# Checkpoint 1
logger.debug("Checkpoint 1: Starting orchestration")
orchestrator = create_orchestrator()
# Checkpoint 2
logger.debug("Checkpoint 2: Creating plan")
# ... execute ...
# Checkpoint 3
logger.debug("Checkpoint 3: Executing tasks")
# ... etcInspect Agent State
from strands import Agent
# Access agent internals for debugging
agent = create_script_agent()
print(f"Model: {agent.model}")
print(f"Tools: {agent.tools}")
print(f"System prompt length: {len(agent.system_prompt)}")
# Execute with debug
result = agent.execute("Test", debug=True)Monitor API Calls
import time
class APIMonitor:
"""Monitor API usage."""
def __init__(self):
self.calls = []
def record_call(self, agent: str, duration: float, tokens: int):
self.calls.append({
"agent": agent,
"duration": duration,
"tokens": tokens,
"timestamp": time.time()
})
def report(self):
print("\n📊 API Usage Report")
print("="*60)
for call in self.calls:
print(f"{call['agent']}: {call['duration']:.2f}s, {call['tokens']} tokens")
print(f"\nTotal calls: {len(self.calls)}")
print(f"Total tokens: {sum(c['tokens'] for c in self.calls)}")Step 6.3: Performance Optimization
1. Enable Agent Caching
Anthropic supports prompt caching:
model = AnthropicModel(
model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929",
max_tokens=4000,
temperature=0.7,
cache_system_prompt=True, # ⬅ Cache the system prompt
)Benefit: 90% cost reduction for repeated calls with same system prompt.
2. Parallel Execution
Run independent tasks concurrently:
import asyncio
async def execute_parallel():
"""Execute social and audio in parallel."""
social_task = asyncio.create_task(
create_social_agent().execute_async(prompt)
)
audio_task = asyncio.create_task(
create_tts_agent().execute_async(prompt)
)
social_result, audio_result = await asyncio.gather(
social_task,
audio_task
)3. Response Streaming
For better UX, stream responses:
agent = Agent(
model=model,
system_prompt=prompt,
enable_streaming=True, # ⬅ Enable streaming
)
for chunk in agent.stream(user_input):
print(chunk, end='', flush=True)4. Token Optimization
def optimize_token_usage():
"""Strategies for reducing token usage."""
# 1. Shorter system prompts
system_prompt = load_optimized_prompt() # Concise version
# 2. Truncate long inputs
def truncate_input(text: str, max_tokens: int = 1000) -> str:
# Estimate: ~4 chars per token
max_chars = max_tokens * 4
if len(text) > max_chars:
return text[:max_chars] + "...[truncated]"
return text
# 3. Use smaller models for simple tasks
simple_model = AnthropicModel(
model="claude-3-haiku-20240307", # Cheaper model
max_tokens=1000
)Step 6.4: Production Deployment
Environment Configuration
# config.py
import os
from typing import Literal
class Config:
"""Production configuration."""
# Environment
ENV: Literal["dev", "staging", "prod"] = os.getenv("ENV", "dev")
# API Keys
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY: str = os.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY", "")
OPENAI_API_KEY: str = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY", "")
TAVILY_API_KEY: str = os.getenv("TAVILY_API_KEY", "")
ELEVENLABS_API_KEY: str = os.getenv("ELEVENLABS_API_KEY", "")
# Rate Limits
MAX_REQUESTS_PER_MINUTE: int = int(os.getenv("MAX_RPM", "60"))
# Timeouts
AGENT_TIMEOUT: int = int(os.getenv("AGENT_TIMEOUT", "120"))
# Logging
LOG_LEVEL: str = os.getenv("LOG_LEVEL", "INFO")
@classmethod
def validate(cls):
"""Validate required configuration."""
missing = []
if not cls.ANTHROPIC_API_KEY:
missing.append("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
if missing:
raise ValueError(f"Missing required config: {', '.join(missing)}")
# Validate on import
Config.validate()Error Monitoring
# monitoring.py
import logging
from typing import Optional
class ErrorMonitor:
"""Monitor and report errors."""
def __init__(self):
self.logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
self.errors = []
def report_error(
self,
error: Exception,
context: dict,
severity: str = "error"
):
"""Report error with context."""
self.errors.append({
"error": str(error),
"type": type(error).__name__,
"context": context,
"severity": severity
})
self.logger.error(
f"{severity.upper()}: {error}",
extra=context,
exc_info=True
)
# In production: send to monitoring service
# self._send_to_sentry(error, context)
def get_error_summary(self) -> dict:
"""Get summary of recent errors."""
return {
"total_errors": len(self.errors),
"by_type": self._group_by_type(),
"recent": self.errors[-10:] # Last 10
}Health Checks
# health.py
from typing import Dict
def health_check() -> Dict[str, str]:
"""Check system health."""
checks = {}
# Check API keys
checks["api_keys"] = "ok" if Config.validate() else "fail"
# Check model access
try:
agent = create_script_agent()
result = agent.execute("test")
checks["anthropic_api"] = "ok"
except Exception as e:
checks["anthropic_api"] = f"fail: {e}"
# Check disk space
import shutil
stat = shutil.disk_usage("/")
free_gb = stat.free / (1024**3)
checks["disk_space"] = "ok" if free_gb > 1 else f"low: {free_gb:.1f}GB"
# Overall status
all_ok = all(v == "ok" for v in checks.values())
checks["status"] = "healthy" if all_ok else "degraded"
return checksStep 6.5: Best Practices Summary
Agent Design
✅ DO:
- Use clear, specific system prompts
- Set appropriate temperature for task type
- Handle errors gracefully
- Log important actions
- Validate inputs and outputs
❌ DON’T:
- Use vague or conflicting instructions
- Ignore token limits
- Let exceptions bubble unhandled
- Skip input validation
- Hardcode API keys
Tool Design
✅ DO:
- Single responsibility per tool
- Type-safe with Pydantic
- Comprehensive error handling
- Clear documentation
- Unit test each tool
❌ DON’T:
- Create overly complex tools
- Skip input validation
- Return unclear errors
- Forget to handle edge cases
- Mix multiple concerns
Orchestration
✅ DO:
- Plan before executing
- Respect dependencies
- Enable parallel execution
- Handle partial failures
- Monitor progress
❌ DON’T:
- Hardcode workflows
- Execute serially when parallel possible
- Stop on optional failures
- Lose execution context
- Skip error recovery
Production
✅ DO:
- Use environment variables
- Implement comprehensive logging
- Add health checks
- Monitor API usage
- Set timeouts and retries
- Cache when appropriate
❌ DON’T:
- Commit API keys
- Skip monitoring
- Ignore rate limits
- Deploy without testing
- Forget error handling
- Leave debug code in prod
Step 6.6: Performance Benchmarks
Typical execution times for the complete pipeline:
| Component | Duration | Tokens | Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research (2 iterations) | 40-60s | ~8,000 | $0.12 |
| Script Generation | 30-45s | ~4,000 | $0.06 |
| Social Media | 15-20s | ~1,500 | $0.02 |
| TTS Audio | 45-90s | N/A | $0.15 |
| Total Pipeline | 2.5-3.5min | ~13,500 | ~$0.35 |
*Approximate costs based on Claude 3.5 Sonnet and ElevenLabs pricing (Oct 2024)
Optimization Results
With optimizations:
- Prompt caching: -90% cost for repeated calls
- Parallel execution: -30% total time (social + audio parallel)
- Token optimization: -20% token usage
- Streaming: Better UX, no speed gain
Step 6.7: Deployment Options
Option 1: Local Execution
# Simple local script
python main.pyUse case: Development, testing, small-scale
Option 2: API Server
# server.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
from app.model.agent_input import PipelineInput
from app.orchestrator_agent.agent import create_orchestrator
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/generate")
async def generate(input: PipelineInput):
orchestrator = create_orchestrator()
result = orchestrator.execute(input)
return result.model_dump()
# Run: uvicorn server:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000Use case: API service, multiple clients
Option 3: Background Jobs
# worker.py
from celery import Celery
from app.model.agent_input import PipelineInput
from app.orchestrator_agent.agent import create_orchestrator
app = Celery('podcast_pipeline')
@app.task
def generate_podcast(input_dict: dict):
input = PipelineInput(**input_dict)
orchestrator = create_orchestrator()
result = orchestrator.execute(input)
return result.model_dump()
# Run: celery -A worker worker --loglevel=infoUse case: Long-running tasks, queue-based processing
Option 4: Serverless
# AWS Lambda handler
def lambda_handler(event, context):
input = PipelineInput(**event)
orchestrator = create_orchestrator()
result = orchestrator.execute(input)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': result.model_dump_json()
}Use case: Event-driven, auto-scaling, pay-per-use
Checkpoint: Final Verification
- All agents working independently
- Full pipeline completes successfully
- Errors are handled gracefully
- Logging is comprehensive
- Performance is acceptable
- Ready for production deployment
Key Takeaways
What You’ve Built
-
5 Specialized Agents:
- Script generation
- Social media creation
- Text-to-speech conversion
- Web research
- Orchestration
-
Tool Integration:
- Built-in tools (fetch_url)
- Custom tools (ElevenLabs)
- External APIs (Tavily)
-
Production Features:
- Error handling and retries
- Token management
- Structured I/O
- Monitoring and logging
-
Advanced Patterns:
- Multi-turn conversations
- Dependency management
- Parallel execution
- Adaptive workflows
Skills Acquired
✅ Agent creation and configuration
✅ Tool development and integration
✅ Error handling strategies
✅ Performance optimization
✅ Production deployment
✅ Multi-agent orchestration
Next Steps
Extend the System
-
Add More Agents:
- Video generation agent
- Translation agent
- Summarization agent
- SEO optimization agent
-
Enhance Tools:
- Add more search providers
- Integrate file storage (S3)
- Add database tools
- Implement webhook notifications
-
Improve Orchestration:
- ML-based task scheduling
- Cost optimization
- Quality assessment
- Auto-retry strategies
Production Deployment
-
Infrastructure:
- Set up monitoring (DataDog, New Relic)
- Configure CI/CD pipeline
- Implement rate limiting
- Add authentication
-
Optimization:
- Profile and optimize slow paths
- Implement caching strategy
- Optimize token usage
- Enable auto-scaling
-
Reliability:
- Add comprehensive tests
- Implement circuit breakers
- Set up alerting
- Create runbooks
Resources
Documentation
Code
Community
Workshop Complete! 🎉
Congratulations! You’ve built a complete multi-agent system with:
- ✅ 5 specialized agents
- ✅ Multiple tool integrations
- ✅ Production-ready patterns
- ✅ Intelligent orchestration
What’s Next?
- ⭐ Star the repository if you found this helpful
- 🔧 Extend the system with your own agents
- 🚀 Deploy to production and share your experience
- 📝 Write about it and help others learn
- 🤝 Contribute back improvements and fixes
Feedback
We’d love to hear from you:
- What did you learn?
- What could be improved?
- What would you like to see next?
Thank you for participating! 🙏
Questions? Reach out to the instructor or community.