Step 3: TTS Agent with Custom Tools (10 minutes)
Code Location: code/v0.4.0/
Time: 30:00-40:00
Goal: Create custom tools for external API integration
Overview
In this step, you’ll learn:
- How to create custom tools from scratch
- Integrate external APIs (ElevenLabs TTS)
- Handle binary data and file operations
- Implement proper error handling
- Track token usage across agents
Why Custom Tools?
Built-in tools cover common cases, but you’ll often need:
- Domain-specific APIs: Your business logic
- Custom integrations: Third-party services
- Specialized processing: Unique data transformations
- Company tools: Internal systems
Architecture
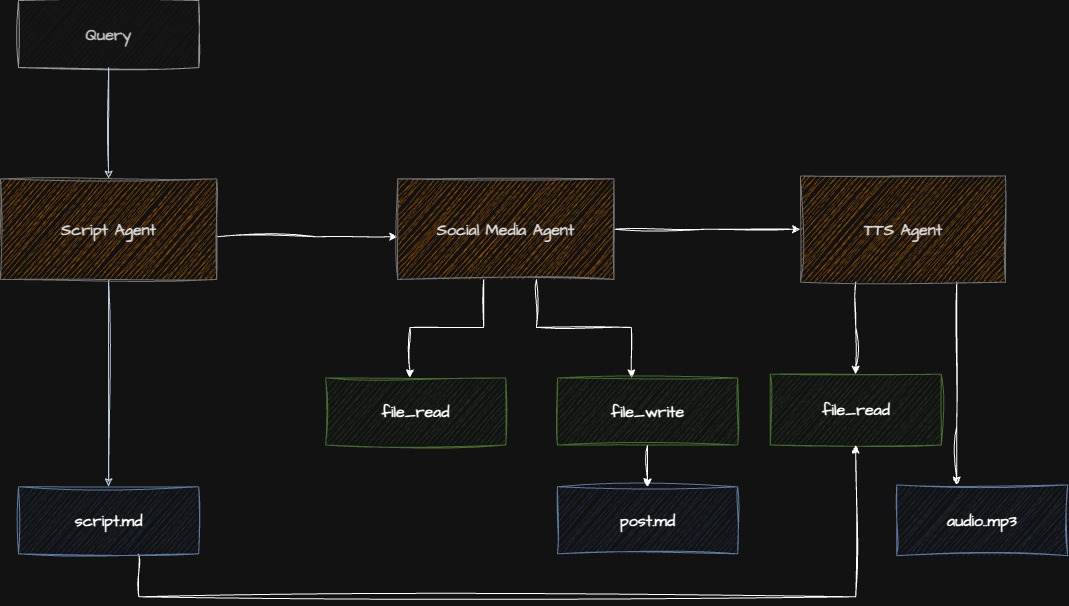
Checkpoint: Starting Point
Before proceeding:
- Completed Step 2
- Navigate to
code/v0.4.0/directory - ElevenLabs API key in
.env
Step 3.1: Understanding Tool Requirements
A good custom tool needs:
- Clear purpose: One specific task
- Type safety: Pydantic validation
- Documentation: Docstrings and descriptions
- Error handling: Graceful failures
- Testing: Unit tests
Step 3.2: Creating a Custom TTS Tool
File: app/tts_agent/tools/elevenlabs_tool.py
"""ElevenLabs text-to-speech tool."""
import os
import logging
from typing import Optional
from pydantic import Field
from elevenlabs import ElevenLabs, VoiceSettings
from strands.tools import tool
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@tool
def text_to_speech(
text: str = Field(description="Text to convert to speech"),
voice_id: str = Field(
default="21m00Tcm4TlvDq8ikWAM", # Rachel voice
description="ElevenLabs voice ID"
),
output_path: str = Field(
default="output.mp3",
description="Path where audio file will be saved"
)
) -> str:
"""
Convert text to speech using ElevenLabs API.
This tool takes text input and generates natural-sounding
speech audio, saving it to a file.
Args:
text: The text to convert to speech
voice_id: ElevenLabs voice identifier (default: Rachel)
output_path: Where to save the audio file
Returns:
Success message with file path
Raises:
ValueError: If API key missing or text empty
RuntimeError: If API call fails
"""
# Validate inputs
if not text or not text.strip():
raise ValueError("Text cannot be empty")
api_key = os.getenv("ELEVENLABS_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
raise ValueError("ELEVENLABS_API_KEY not found in environment")
try:
# Initialize client
client = ElevenLabs(api_key=api_key)
logger.info(f"🎵 Generating audio for {len(text)} characters...")
# Generate audio
audio_generator = client.text_to_speech.convert(
text=text,
voice_id=voice_id,
model_id="eleven_multilingual_v2",
voice_settings=VoiceSettings(
stability=0.5,
similarity_boost=0.75,
style=0.0,
use_speaker_boost=True
)
)
# Write to file
with open(output_path, "wb") as f:
for chunk in audio_generator:
f.write(chunk)
logger.info(f"✅ Audio saved to {output_path}")
return f"Successfully generated audio and saved to {output_path}"
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ TTS generation failed: {e}")
raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to generate speech: {str(e)}")Tool Design Breakdown
1. Decorator: @tool makes function available to agents
2. Type Hints: Pydantic Field for validation and description
3. Docstring: Agents read this to understand tool purpose
4. Validation: Check inputs before API call
5. Error Handling: Specific exceptions with context
6. Logging: Track execution for debugging
Step 3.3: Installing External Dependencies
File: pyproject.toml
[project]
dependencies = [
"strands-agents>=0.3.0",
"strands-agents-tools>=0.1.0",
"elevenlabs>=1.0.0", # ⬅ Add TTS library
"python-dotenv>=1.0.0",
# ... other dependencies
]uv syncStep 3.4: Creating the TTS Agent
File: app/tts_agent/agent.py
"""Text-to-speech agent."""
from strands import Agent
from strands_ai.models.anthropic import AnthropicModel
from app.tts_agent.tools.elevenlabs_tool import text_to_speech
def create_tts_agent() -> Agent:
"""
Create TTS agent with custom ElevenLabs tool.
Returns:
Configured Agent with TTS capability
"""
model = AnthropicModel(
model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929",
max_tokens=2000,
temperature=0.3, # Lower temperature for tool use
)
# Load prompt
with open("app/tts_agent/prompt.md", "r") as f:
system_prompt = f.read()
# Create agent with custom tool
agent = Agent(
model=model,
system_prompt=system_prompt,
tools=[text_to_speech], # ⬅ Our custom tool
enable_streaming=False,
)
return agentStep 3.5: Writing the TTS Prompt
File: app/tts_agent/prompt.md
# Audio Production Agent
You are an audio production specialist responsible for converting
podcast scripts into speech audio files.
## Your Role
Process podcast scripts and generate high-quality audio using
text-to-speech technology.
## Tool Available
You have access to `text_to_speech` tool:
**When to use**:
- User provides script text
- Audio file generation is requested
- Converting text to audio format
**Parameters**:
- `text`: The script content (required)
- `voice_id`: Voice identifier (optional, defaults to Rachel)
- `output_path`: Save location (optional, defaults to output.mp3)
## Processing Guidelines
1. **Script Preparation**:
- Remove formatting markers (e.g., [INTRO], [HOST])
- Clean up speaker labels
- Ensure smooth text flow
- Remove stage directions
2. **Voice Selection**:
- Default voice (Rachel) works for most content
- Use consistent voice throughout
3. **Quality Checks**:
- Verify text is readable
- Check for special characters that may cause issues
- Ensure reasonable length (under 100k characters)
## Output
After generating audio:
1. Confirm successful generation
2. Report file location
3. Provide file size if available
4. Note any warnings or issues
## Error Handling
If generation fails:
- Explain the error clearly
- Suggest fixes (e.g., text too long, API issues)
- Offer alternative approachesStep 3.6: Integrating into Pipeline
Update: main.py
"""Main entry point for the rooting pipeline."""
import logging
from app.script_agent.agent import create_script_agent
from app.social_agent.agent import create_social_agent
from app.tts_agent.agent import create_tts_agent # ⬅ Add
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def main():
"""Execute the complete pipeline."""
topic = "Building Multi-Agent Systems"
# Step 1: Generate script
logger.info("🎙️ Generating podcast script...")
script_agent = create_script_agent()
script = script_agent.execute(topic).output
print(f"✅ Script: {len(script)} chars\n")
# Step 2: Generate social post
logger.info("📱 Generating social media post...")
social_agent = create_social_agent()
social_post = social_agent.execute(
f"Create a LinkedIn post for: {script[:300]}..."
).output
print(f"✅ Social post created\n")
# Step 3: Generate audio
logger.info("🎵 Generating audio...")
tts_agent = create_tts_agent()
audio_result = tts_agent.execute(
f"Convert this script to audio: {script}"
)
print(f"✅ {audio_result.output}\n")
print("="*80)
print("PIPELINE COMPLETE")
print("="*80)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Step 3.7: Running the Complete Pipeline
python main.pyExpected Output:
INFO - 🎙️ Generating podcast script...
✅ Script: 3421 chars
INFO - 📱 Generating social media post...
✅ Social post created
INFO - 🎵 Generating audio...
INFO - 🎵 Generating audio for 3421 characters...
INFO - ✅ Audio saved to output.mp3
✅ Successfully generated audio and saved to output.mp3
================================================================================
PIPELINE COMPLETE
================================================================================Check the generated file:
ls -lh output.mp3
# Should show audio file with size
# Play it (macOS)
afplay output.mp3
# Play it (Linux)
mpg123 output.mp3Checkpoint: Verify Custom Tool
- Tool imports successfully
- Agent can call the tool
- Audio file is generated
- File is playable
- Errors are handled gracefully
Common Issues & Solutions
Issue: ElevenLabs Import Error
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'elevenlabs'Solution: Install dependency
uv add elevenlabsIssue: API Key Not Found
ValueError: ELEVENLABS_API_KEY not foundSolution: Add to .env
echo "ELEVENLABS_API_KEY=your_key_here" >> .envIssue: Audio File Empty
Possible causes:
- Text was empty after processing
- API rate limit hit
- Invalid voice ID
Solution: Add detailed logging
logger.info(f"Text length: {len(text)}")
logger.info(f"Voice ID: {voice_id}")Issue: Tool Not Called
Solution: Make prompt more explicit
## Instructions
ALWAYS use the text_to_speech tool when processing a script.
Do not just acknowledge - actually generate the audio.Exercise: Add Voice Selection
Enhance the tool with multiple voice options:
VOICE_OPTIONS = {
"rachel": "21m00Tcm4TlvDq8ikWAM",
"adam": "pNInz6obpgDQGcFmaJgB",
"sam": "yoZ06aMxZJJ28mfd3POQ",
}
@tool
def text_to_speech(
text: str,
voice_name: str = Field(
default="rachel",
description="Voice name: rachel, adam, or sam"
),
output_path: str = "output.mp3"
) -> str:
voice_id = VOICE_OPTIONS.get(voice_name, VOICE_OPTIONS["rachel"])
# ... rest of implementationUnderstanding Binary Data Handling
TTS returns audio bytes - here’s how to handle them:
# Stream and write chunks
with open(output_path, "wb") as f: # 'wb' = write binary
for chunk in audio_generator:
f.write(chunk)
# Or collect all and write once
audio_bytes = b"".join(audio_generator)
with open(output_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(audio_bytes)Key Concepts Review
What You Learned
- Custom Tool Creation: Building tools from scratch
- External API Integration: Calling third-party services
- Binary Data: Handling non-text data
- Error Handling: Robust failure management
- Tool Documentation: Making tools discoverable
Tool Best Practices
DO:
- ✅ Validate inputs thoroughly
- ✅ Provide clear descriptions
- ✅ Handle errors gracefully
- ✅ Log important steps
- ✅ Return meaningful messages
DON’T:
- ❌ Assume inputs are valid
- ❌ Let exceptions bubble uncaught
- ❌ Return cryptic messages
- ❌ Skip documentation
- ❌ Ignore edge cases
Advanced Topics (Time Permitting)
Async Tools
from strands.tools import async_tool
@async_tool
async def async_text_to_speech(text: str) -> str:
"""Async version for concurrent processing."""
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
# Async API calls
...Tool Caching
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=100)
def get_voice_id(voice_name: str) -> str:
"""Cache voice ID lookups."""
return VOICE_OPTIONS.get(voice_name)Progress Reporting
@tool
def text_to_speech_with_progress(text: str) -> str:
"""TTS with progress updates."""
chunks = len(text) // 1000
for i, chunk in enumerate(text_chunks):
progress = (i + 1) / chunks * 100
logger.info(f"Progress: {progress:.0f}%")
# Process chunk
return "Complete!"Production Considerations
- ✅ Rate limiting: Track API calls
- ✅ Cost management: Monitor usage
- ✅ Caching: Cache expensive operations
- ✅ Retry logic: Handle transient failures
- ✅ Timeouts: Set reasonable limits
- ✅ Monitoring: Track success rates
Next Steps
You’ve mastered custom tool creation! You now understand:
- How to build tools for any API
- Binary data handling
- Proper error management
- Tool documentation patterns
Ready for complex workflows? Continue to Step 4: Research Agent
Additional Resources
Questions for Discussion
- What other custom tools would be useful for this pipeline?
- How would you handle tool failures that block the pipeline?
- When should you use sync vs async tools?
- How would you test custom tools in isolation?
Time Check: You should be at approximately 40 minutes. Take a short break before diving into the research agent.