Step 2: Social Media Agent with Built-in Tools (15 minutes)
Code Location: code/v0.3.0/
Time: 15:00-30:00
Goal: Learn how to add tools to agents using Strands built-in tools
Overview
In this step, you’ll learn:
- How to add tools to agents
- Using Strands built-in tool library
- Tool configuration and parameters
- Multi-tool agent workflows
- Switching between model providers
Why Tools Matter
Tools extend agent capabilities beyond text generation:
- Web Access: Fetch URLs, search the web
- File Operations: Read/write files
- API Integration: Call external services
- Data Processing: Manipulate structured data
Architecture Evolution
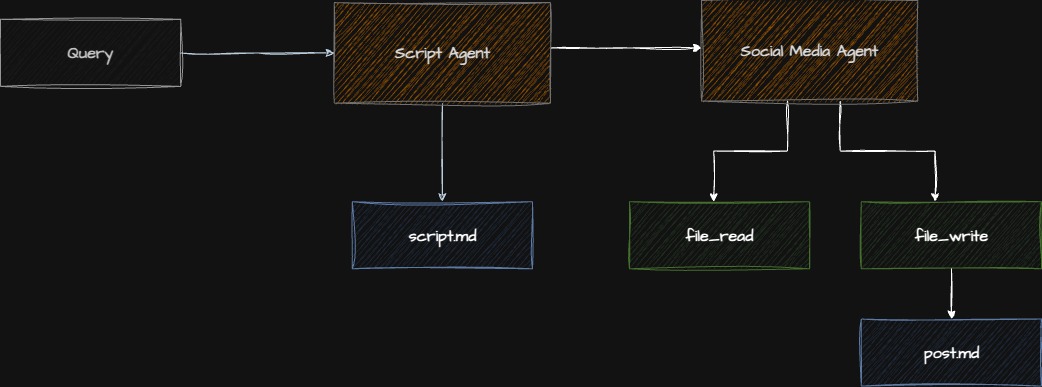
Checkpoint: Starting Point
Before proceeding:
- Completed Step 1
- Navigate to
code/v0.3.0/directory - OpenAI API key added to
.env(optional)
Step 2.1: Understanding Built-in Tools
Strands provides a curated tool library via strands-agents-tools:
Available Tools:
web_search: Search the web (multiple providers)fetch_url: Retrieve web page contentread_file: Read local fileswrite_file: Create/update files- Many more…
Why Use Built-in Tools?
✅ Production-ready: Tested and maintained
✅ Consistent API: Standard interface
✅ Type-safe: Pydantic validation
✅ Error handling: Built-in retry logic
Step 2.2: Installing Tool Dependencies
File: pyproject.toml
[project]
dependencies = [
"strands-agents>=0.3.0",
"strands-agents-tools>=0.1.0", # ⬅ Add this
"python-dotenv>=1.0.0",
# ... other dependencies
]Install:
uv syncStep 2.3: Creating the Social Media Agent
File: app/social_agent/agent.py
"""Social media content generation agent."""
import os
from strands import Agent
from strands_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
from strands_ai.models.anthropic import AnthropicModel
from strands_agents_tools.web import fetch_url
def create_social_agent(use_openai: bool = False) -> Agent:
"""
Create social media content agent with web tools.
Args:
use_openai: If True, use OpenAI; otherwise use Anthropic
Returns:
Configured Agent with web fetch capability
"""
# Choose model provider
if use_openai and os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"):
model = OpenAIModel(
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.7,
)
else:
model = AnthropicModel(
model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929",
max_tokens=4000,
temperature=0.7,
)
# Load prompt
with open("app/social_agent/prompt.md", "r") as f:
system_prompt = f.read()
# Create agent WITH TOOLS
agent = Agent(
model=model,
system_prompt=system_prompt,
tools=[fetch_url], # ⬅ Add tools here
enable_streaming=False,
)
return agentKey Changes from Step 1
- Import tools:
from strands_agents_tools.web import fetch_url - Add to agent:
tools=[fetch_url] - Multiple models: Support both OpenAI and Anthropic
Step 2.4: Writing the Social Media Prompt
File: app/social_agent/prompt.md
# Social Media Content Creator
You are a social media expert specializing in LinkedIn posts that drive engagement.
## Your Role
Create compelling LinkedIn posts that:
- Hook readers in the first line
- Provide valuable insights
- Include relevant hashtags
- Encourage engagement (likes, comments, shares)
- Are optimized for LinkedIn's algorithm
## Tools Available
You have access to `fetch_url` tool to:
- Research topics by fetching relevant articles
- Verify facts from authoritative sources
- Get inspiration from successful posts
- Stay current with latest trends
**When to use tools**:
- User provides a URL to reference
- You need current information
- Research would improve post quality
- Fact-checking is important
## Post Format
### Structure
1. **Hook** (first 2 lines): Grab attention
2. **Value** (3-5 paragraphs): Core insights
3. **Call-to-Action**: Encourage interaction
4. **Hashtags**: 3-5 relevant tags
### Style Guidelines
- Short paragraphs (1-3 sentences)
- Use emojis strategically (not excessively)
- Break up text with line breaks
- Include personal anecdotes when relevant
- Ask engaging questions
### Length
- Optimal: 150-300 words
- Maximum: 400 words
## Example Output
🚀 Just discovered why 80% of AI agents fail in production...
After building 20+ agent systems, I've learned the hard way that
[tool usage insight].
Here's what actually matters:
→ Clear agent boundaries
→ Robust error handling
→ Token management
→ Testing at scale
The breakthrough came when I realized [key insight].
What's your experience with AI agents? Share below! 👇
#AIEngineering #LLMs #AgentArchitecture
## Output
Provide ONLY the LinkedIn post. No meta-commentary.Prompt Design Notes
- Tool guidance: Explain when/how to use tools
- Format examples: Show desired output structure
- Style guide: Define tone and formatting
- Constraints: Set length and quality expectations
Step 2.5: Understanding Tool Execution Flow
When the agent runs:
1. Agent receives: "Create a post about https://example.com/article"
2. Agent decides: "I should fetch this URL first"
3. Tool execution: fetch_url(url="https://example.com/article")
4. Tool returns: Article content
5. Agent processes: Reads content, extracts insights
6. Agent generates: LinkedIn post based on content
7. Final output: Formatted postStep 2.6: Running the Social Agent
Update: main.py
"""Main entry point for the rooting pipeline."""
import logging
from app.script_agent.agent import create_script_agent
from app.social_agent.agent import create_social_agent # ⬅ Add
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def main():
"""Execute the pipeline."""
# Generate script
logger.info("🎙️ Generating podcast script...")
script_agent = create_script_agent()
script_result = script_agent.execute(
"Building Multi-Agent Systems with Python"
)
print(f"\n📝 Script generated ({len(script_result.output)} chars)\n")
# Generate social media post
logger.info("📱 Generating social media post...")
social_agent = create_social_agent()
social_result = social_agent.execute(
f"Create a LinkedIn post promoting this podcast: {script_result.output[:500]}..."
)
print("\n" + "="*80)
print("SOCIAL MEDIA POST")
print("="*80 + "\n")
print(social_result.output)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Run it:
python main.pyStep 2.7: Testing Tool Usage
Create a test that requires tool usage:
# Test with URL
social_agent = create_social_agent()
result = social_agent.execute(
"Create a LinkedIn post about https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-3-5-sonnet"
)
print(result.output)Watch the logs - you should see tool invocation:
INFO - Agent calling tool: fetch_url
INFO - Tool fetch_url completed
INFO - Generating response with tool resultsCheckpoint: Verify Tool Integration
- Agent runs successfully
- Tools are properly imported
- Agent can fetch URLs when provided
- Post format matches guidelines
Common Issues & Solutions
Issue: Tool Not Found
ValueError: Tool 'fetch_url' not foundSolution: Install tools package
uv add strands-agents-toolsIssue: Tool Execution Fails
ToolExecutionError: Failed to fetch URLSolution: Check URL is accessible, handle errors
try:
result = agent.execute(prompt)
except ToolExecutionError as e:
logger.error(f"Tool failed: {e}")Issue: Agent Doesn’t Use Tools
Reasons:
- Prompt doesn’t mention tools
- Task doesn’t require tools
- Tool name not clear
Solution: Be explicit in prompt
## When to Use Tools
ALWAYS use fetch_url when the user provides a URL.
Use it to gather facts before writing.Exercise: Add More Tools
Try adding multiple tools:
from strands_agents_tools.web import fetch_url, web_search
from strands_agents_tools.file import write_file
agent = Agent(
model=model,
system_prompt=prompt,
tools=[fetch_url, web_search, write_file], # Multiple tools
)Test it:
result = agent.execute(
"Search for 'AI agents best practices', then create a LinkedIn post and save it to post.txt"
)Understanding Tool Design
Good tools are:
- Single purpose: Do one thing well
- Type-safe: Pydantic models for inputs/outputs
- Documented: Clear descriptions
- Idempotent: Same input = same output (when possible)
- Error-aware: Handle failures gracefully
Tool Anatomy
from pydantic import Field
from strands.tools import tool
@tool
def fetch_url(
url: str = Field(description="URL to fetch")
) -> str:
"""
Fetch content from a web URL.
Args:
url: The URL to retrieve
Returns:
Page content as text
"""
# Implementation
...Key Concepts Review
What You Learned
- Tool Integration: Adding tools to agents
- Built-in Tools: Using Strands tool library
- Multi-Model Support: Switching between providers
- Tool Execution: How agents use tools
- Prompt Engineering: Guiding tool usage
Tool Selection Guidelines
Use built-in tools when:
- Common functionality (web, files, APIs)
- Production stability matters
- You need standard interface
Create custom tools when:
- Unique business logic required
- Specific API integration needed
- Domain-specific operations
Advanced Topics (Time Permitting)
Conditional Tool Usage
# Agent decides when to use tools based on context
prompt = """
Use fetch_url ONLY if:
1. User provides a URL explicitly
2. Current information is critical
3. Fact verification is needed
Otherwise, use your training knowledge.
"""Tool Configuration
from strands_agents_tools.web import fetch_url
# Configure tool behavior
configured_tool = fetch_url.with_config(
timeout=10,
max_retries=3,
follow_redirects=True
)
agent = Agent(tools=[configured_tool])Tool Chaining
# Agent can chain multiple tools
prompt = """
1. Search for topic with web_search
2. Fetch top 3 results with fetch_url
3. Synthesize into LinkedIn post
4. Save to file with write_file
"""Production Considerations
- ✅ Rate limiting: Respect API limits
- ✅ Caching: Cache tool results when appropriate
- ✅ Timeouts: Set reasonable timeouts
- ✅ Error handling: Graceful degradation
- ✅ Cost tracking: Monitor tool usage costs
- ✅ Security: Validate tool inputs
Comparison: OpenAI vs Anthropic
OpenAI (GPT-4o):
- ✅ Fast tool selection
- ✅ Good at parallel tools
- ❌ More expensive
- ❌ Sometimes overuses tools
Anthropic (Claude):
- ✅ Excellent reasoning
- ✅ Conservative tool use
- ✅ Better cost/performance
- ❌ Slightly slower
Recommendation: Start with Claude, switch to OpenAI if tool performance critical.
Next Steps
You’ve mastered tool integration! You now understand:
- How to add built-in tools to agents
- When and how agents use tools
- Multi-model agent patterns
- Tool-augmented workflows
Ready to create custom tools? Continue to Step 3: TTS Agent with Custom Tools
Additional Resources
Questions for Discussion
- When should agents use tools vs rely on training data?
- How do you handle tool failures gracefully?
- What’s the tradeoff between tool accuracy and speed?
- How would you test agent tool usage?
Time Check: You should be at approximately 30 minutes. Take a quick break if needed before moving to custom tools.